Eco-Innovation in Cardboard and Packaging Disposal
Posted on 18/10/2025
In the contemporary world, sustainability and environmental responsibility are no longer optional -- they're imperative. As global packaging waste surges, businesses and consumers alike are rethinking their choices. Among the many environmental challenges, disposal of cardboard and packaging containers stands out due to sheer volume and resource intensity. This is where eco-innovation in cardboard and packaging disposal comes into play, promising to reshape the future of waste management, recycling, and product design.
Understanding the Impact of Cardboard and Packaging Waste
Modern commerce relies heavily on shipping materials, much of which is made of cardboard and various types of packaging. However, with every package delivered comes an environmental cost.
- Cardboard accounts for nearly 31% of all solid municipal waste globally.
- Around 80 billion cardboard boxes are used annually in the U.S. alone.
- Poor disposal habits lead to landfills overburdened with recyclable material.
- Traditional packaging can take centuries to decompose, causing pollution and occupying landfill space.
Eco-friendly innovation in packaging waste disposal not only helps the environment but can also foster economic efficiency and brand reputation for businesses.

What is Eco-Innovation?
Eco-innovation refers to the development of products, processes, and systems that significantly reduce environmental impacts. In the context of cardboard and packaging disposal, it means rethinking how materials are designed, used, disposed of, and ultimately reintroduced into the economy. Eco-innovative practices can include using renewable materials, enhancing recyclability, and inventing new disposal technologies.
The Principles of Eco-Innovation in Packaging
- Reduce: Minimizing the amount of material used in packaging production.
- Reuse: Designing packages for multiple life cycles or secondary uses.
- Recycle: Ensuring that packaging is easy to deconstruct and process into new materials.
- Recover: Extracting energy or resources from used packaging via composting or incineration with energy recovery.
Cardboard: An Eco-Friendly Ally or Wasteful Enemy?
Cardboard, often made from wood pulp, is renewable and *biodegradable* -- but only when disposed of properly. Its recyclability gives it an edge over plastic, but contamination by food, oils, or adhesives can prevent effective recycling.
- Corrugated cardboard is the most widely recycled packaging material.
- Properly recycled cardboard can create new packaging, paper, or even be used in 3D printing filaments.
- Poor sorting or wet/dirty cardboard leads to waste and energy inefficiency.
Thus, innovation in cardboard disposal is essential for harnessing its environmental advantages.
Advanced Recycling Technologies for Cardboard and Packaging
One of the leading trends in eco-innovation for packaging waste disposal is the adoption of advanced recycling technologies. These innovations improve sorting, processing, and material recovery efficiency.
Automated Sorting Systems
Modern recycling facilities are now equipped with AI-powered sorting systems. These use cameras, image recognition, and robotics to separate cardboard from mixed waste streams, drastically reducing contamination and improving recycling rates.
De-Inking and Cleaning Technologies
Innovations in de-inking technology enable removal of impurities from printed or coated cardboard, making recycled material purer and more valuable. Some facilities use bio-based solvents or enzymatic cleaners for safer, eco-friendly decontamination processes.
Mechanical & Chemical Recycling
- Mechanical Recycling: The most common method, it involves shredding and pulping cardboard for reuse. Efficient sorting and cleaning are key to high-quality output.
- Chemical Recycling: Emerging techniques use chemicals to break down complex packaging composites, allowing extraction of pure cellulose fibers even from heavily treated or laminated cardboard.
By combining mechanical and chemical recycling, facilities can process previously untreatable materials, expanding the reach of eco-innovation in packaging disposal.
Biodegradable and Compostable Packaging: Beyond Cardboard
While cardboard dominates, eco-innovative packaging now encompasses an array of biodegradable and compostable solutions. These innovations are designed to return to the earth without leaving toxic residues, supporting circular economy goals.
Examples of Eco-Innovative Packaging Materials
- Molded pulp packaging: Made from recycled paper, it's compostable and strong enough to replace Styrofoam and hard plastic.
- Starch-based packaging: Utilizes potato or corn starch, breaking down in industrial and home compost bins.
- Mycelium packaging: Grown from mushroom roots, it's renewable, compostable, and customizable for product protection.
Brands switching to these materials reduce traditional cardboard waste while contributing to healthier soils and less polluted landfills.
Designing for Disassembly and Recycling
A key element of eco-innovation in cardboard packaging and disposal is product design. By considering end-of-life scenarios at the design stage, manufacturers can drastically improve packaging sustainability.
Design Strategies for Eco-Friendly Packaging
- Mono-materials: Using a single type of cardboard or paper improves recycling efficiency.
- Easy separation: Components (plastic windows, inserts) should be easy for consumers to remove.
- Minimal adhesives and inks: Reducing chemicals enables cleaner recycling and composting.
- Clever folding: Designing packages that require less tape or glue without sacrificing security.
- Clear disposal instructions: Packaging should feature easy-to-understand recycling symbols and guidelines.
Consumer Engagement and Behavioral Change
No matter how innovative, new materials and technologies require consumer participation to reach their full potential. Eco-innovation in packaging waste disposal only succeeds if customers are aware of proper sorting, cleaning, and recycling practices.
Strategies to Influence Consumer Behavior
- Clear labeling: Use universal recycling symbols and QR codes linking to disposal guides.
- Deposit return schemes: Incentivize returning boxes and packaging for reuse or recycling.
- Education campaigns: Inform users of the environmental impact and correct disposal methods.
- Brand responsibility: Companies can offer rewards for eco-friendly behavior.
Fostering a waste-conscious culture is vital for the advancement of eco-innovation in cardboard and packaging disposal.
Case Studies: Leaders in Eco-Innovation for Packaging Waste Disposal
Amazon's Frustration-Free Packaging Program
- Focuses on easy-to-open, minimal packaging using only recyclable materials.
- Encourages suppliers to design products with fully recyclable cardboard shipping boxes.
- Reportedly has saved millions of cardboard boxes and tons of plastic packaging since its launch.
IKEA's Circular Packaging Design
- IKEA now uses corrugated cardboard that's strong enough to replace foam and plastic, while being fully recyclable.
- The company also pilots packaging take-back programs and facilitates cardboard recycling in stores.
Loop and Zero-Waste Initiatives
- Loop enables reuse by delivering products in durable containers and collecting empties for cleaning and reuse.
- This reduces single-use packaging waste, including cardboard and composite materials.
The Role of Policy and Regulation
Government intervention plays a critical role in scaling eco-innovative packaging and disposal. Many countries and regions enact regulations mandating minimum recycled content, restricting certain materials, and holding producers accountable for end-of-life waste management.
Producer Responsibility and EPR Schemes
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): Laws that require manufacturers to cover the cost of collecting, sorting, and recycling their waste packaging.
- Incentivizes eco-friendly innovation in packaging design and disposal methods.
Bans and Mandates
- Some regions prohibit single-use plastics and non-recyclable packaging altogether.
- Mandates for eco-labeling inform consumers and encourage sustainable choices.
Comprehensive regulatory frameworks foster investment and adoption of innovative cardboard and packaging waste disposal solutions.
Digital Innovation: Blockchain and Smart Tracking
Digital technologies are transforming the recycling and waste management landscape. By integrating blockchain, IoT, and smart sensors, the entire cardboard and packaging life cycle can be optimized.
- Blockchain-based traceability: Every package can be tracked from production to disposal, ensuring responsible recycling.
- Smart bins and IoT: Sensors report fill levels and contamination rates, allowing efficient collection and better recycling outcomes.
- AI-powered sorting apps: Help consumers sort waste correctly using their smartphones.
These innovations make both the process and outcomes of eco-innovative packaging disposal more transparent and effective.
Challenges and Barriers to Eco-Innovation in Cardboard and Packaging Disposal
- Infrastructure Gaps: Not all regions have access to advanced recycling systems or composting facilities.
- Cost: New eco-packaging materials and technologies are often more expensive, at least initially.
- Contamination: Mixed or dirty waste still impairs recycling efficiency.
- Consumer Misunderstanding: Confusion over recycling protocols leads to misplaced efforts.
However, with growing regulatory pressure, consumer demand, and technological breakthroughs, these barriers are shrinking over time.

The Future: Towards a Circular Cardboard and Packaging Economy
The vision driving eco-innovation in cardboard and packaging disposal is a circular economy, where materials remain in use for as long as possible, extracting maximum value before safe return to the environment.
- Cardboard is designed for recycling or composting from the start.
- Consumers actively participate in sorting and returning used packaging.
- Producers innovate with renewable, biodegradable, and reusable materials.
- Smart waste management systems close the loop efficiently and transparently.
From boardroom strategy to recycling bin, every step counts.
Conclusion: A Greener Tomorrow Through Eco-Innovation
The intersection of eco-innovation and cardboard/packaging disposal represents one of the most immediate opportunities for environmental improvement. By leveraging technology, smart design, consumer engagement, and robust policy, we can dramatically cut waste and greenhouse emissions while conserving vital resources.
In the future, success will belong to those who integrate eco-friendly practices across the packaging lifecycle. From designers and manufacturers to consumers and policymakers, every stakeholder has a crucial role to play in transforming cardboard and packaging from environmental liabilities into assets for a sustainable world.
To contribute, start by choosing eco-labelled products, sorting waste carefully, and supporting brands and policies that prioritize eco-innovative disposal solutions. Together, we can build a future where packaging protects products -- and the planet.
Latest Posts
Long-Term Clutter Control: Practical Advice for Lasting Order
Eco-Innovation in Cardboard and Packaging Disposal
Avoid Landfills: Guide to Proper Pot and Pan Recycling
 020 3875 4109
020 3875 4109 020 3875 4109
020 3875 4109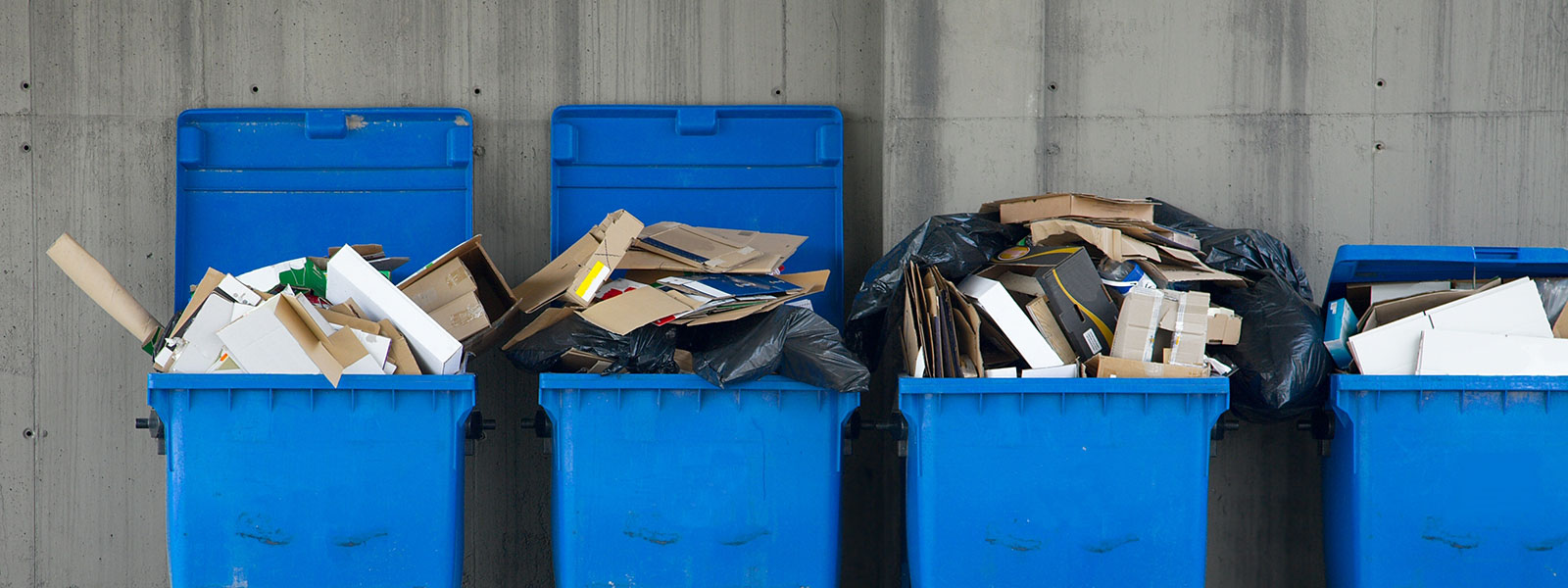

 House clearance
House clearance Rubbish collection
Rubbish collection





